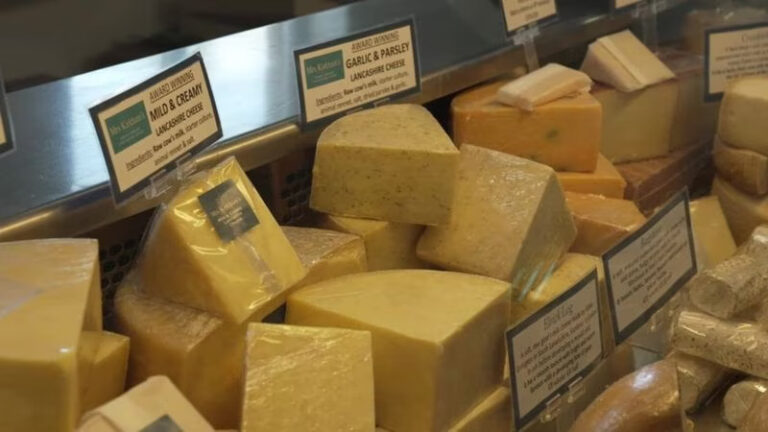
Despite generally being considered safe, stone fruit faces contamination risks leading to multi-state outbreaks. Current practices, including wax coatings with a fungicide, fall short against Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes, prompting the need for enhanced safety measures.
A new project funded by the Center for Produce Safety (CPS) explores incorporating food-grade antimicrobials into wax coatings applied to stone fruit. Researchers aim to improve safety by addressing the limitations of current coatings against specific pathogens, such as Salmonella and Listeria. The project involves screening various antimicrobials, adjusting pH levels, and testing antimicrobial-enhanced coatings on peaches to evaluate their effectiveness.
Funded by $324,925 from the Center for Produce Safety, the project involves collaboration with an Industry Advisory Council to guide and support the research. Results from the testing phase on peaches in 2023 will be validated during the 2024 California peach harvest. Dr. Qixin Zhong expresses optimism about the potential impact on industry practices, hoping the research will provide valuable insights for safer stone fruit handling and storage.
Source: Food Safety News
Reach out to Fresh Group Food Safety And Quality Consulting for any inquiries related to food quality and safety.